A group from Department of Medicine, Columbia University, New York, etc. has reported that in COVID-19 patnents, urinary Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin (uNGAL) quantitatively associated with histopathological injury (ATI), the loss of kidney function (AKI), and the severity of patient outcomes.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8497954/
Notably, COVID-19 patients were 2.6-times more likely to present with acute tubular injury (ATI) (35.2% vs. 13.6%, P < 0.0001), 3.9-times more likely to have sustained functional kidney failure (AKI) (17.5% vs. 4.5%, P < 0.0001) and 1.8-times more likely to have more severe disease (Acute Kidney Injury Network (AKIN) stages 2-3, 12.5% vs. 6.8%, P < 0.01). Thus, although loss of kidney function is a common feature of COVID-19 infection, serum creatinine (SCr) is not a sensitive or specific marker of kidney injury.
For example, SCr can only detect kidney dysfunction in retrospect, after enough time has elapsed for the accumulation of SCr to a diagnostic threshold. In addition, clinically significant changes in SCr may not occur in subtotal or focal kidney damage as a result of compensatory changes in uninjured nephrons which can attenuate the rise in SCr. Even when elevations in SCr are apparent, evidence of tubular injury may be lacking, for example in the presence of volume depletion, a common presentation in patients with COVID-19 associated diarrhea. A rise in SCr may also be confounded by the incidence of rhabdomyolysis in COVID-19, which enhances creatinine production.
So, authors has studied the performance of urinary NGAL (uNGAL) and urinary KIM-1 (uKIM-1) in a large cohort of acute COVID-19 patients (444 patients) presenting to the Columbia University Emergency Department at the peak of the New York City pandemic (March-April 2020).
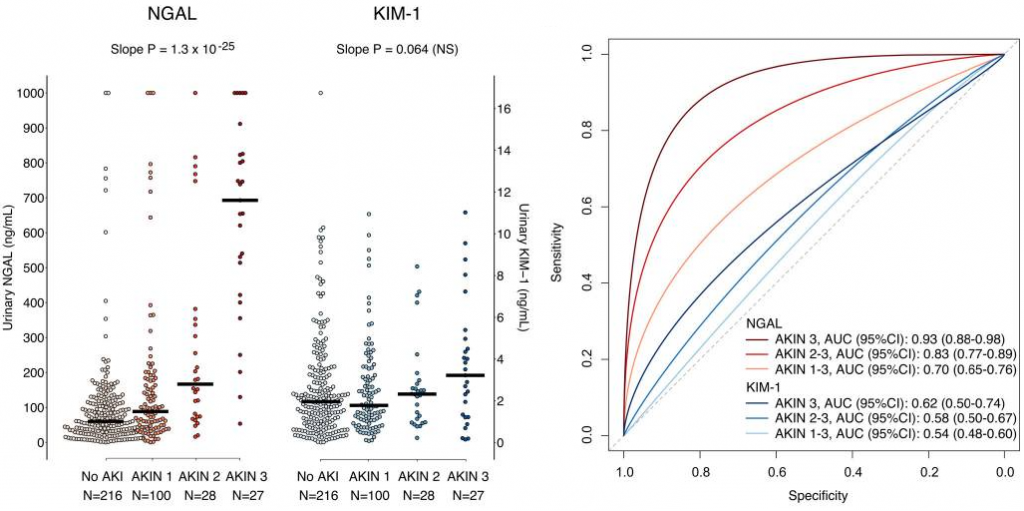
As a result, uNGAL, but not uKIM-1, was associated with the severity of AKI (AKIN stage) as shown below. uNGAL levels increased in a stepwise manner with increasing AKIN stage (P < 0.0001). Similarly, the ROC curve for uNGAL progressively increased with higher AKIN stages (0.70-0.93). uNGAL had 80% specificity and 75% sensitivity to diagnose AKIN stage 2 or 3 at a cutoff level of 150ng/mL.