A group from College of Life Science, South-Central University for Nationalities, Wuhan, China, etc. has reported that Acinetobacter pittii gp-1 promoted soybean growth with its P-stabilization and secretion of indole acetic acid.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8498572/
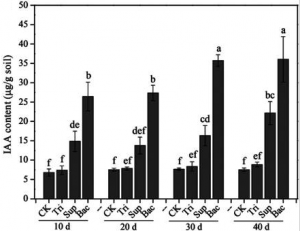
Acinetobacter pittii gp-1 isolated from agricultural soils is known as a P-solubilizing rhizobacterium, and actually the inoculation of Acinetobacter pittii gp-1 promoted soybean growth significantly as shown below.
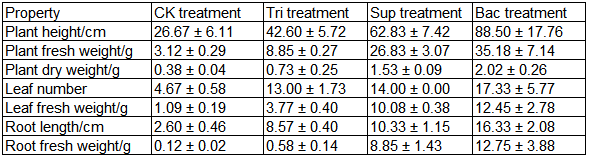
200 g of sieved soil + 100 ml of sterile water (CK treatment)
195 g of sieved soil + 5 g of tricalcium phosphate (TCP) + 100 ml of sterile water (Tri treatment)
200 g of sieved soil + 10 ml of bacterial suspension (107 cfu/ml) + 90 ml of sterile water (Sup treatment)
195 g of sieved soil + 5 g of tricalcium phosphate (TCP) + 10 ml of Acinetobacter suspension (107 cfu/ml) + 90 ml of sterile water (Bac treatment)
The indole acetic acid, which is known as phytohormone, content was significantly higher in Bac treatment than in other treatments, which also might promote soybean growth.