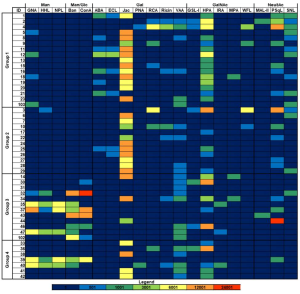
Lectin staining is significantly different between formalin-fixed tissue samples and frozen tissue samples
A group from Department of Gastroenterological surgery, Gifu University School of Medicine, Gifu, Japan, has reported about differences in glycocalyx morphology and composition in frozen and formalin-fixed liver tumor sections.
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0344033824005715?via%3Dihub
It was found that surprisingly, there were many differences in lectin staining findings between frozen and formali-fixed tissue preparations, suggesting that FFPE processing affects lectin receptors, rendering frozen sections more reliable for accurate lectin staining.
From the lectin staining in frozen sections, the followings were found:
Normal hepatocytes showed strongly positive staining for PNA, RCA I, SBA, UEA I, GSL I, succinylated WGA, ECL, GSL II, STL, and VVL.
In contrast, hepatocellular carcinoma samples were strongly positive for DSL and GSL II.
Normal hepatocytes were positive for multiple GalNAc-related lectins (PNA, SBA, GSL I, and VVL), but these were not detected in hepatocellular carcinoma samples.
It was also found that DBA and UEA I staining were strongly positive in liver metastases from colorectal cancer and in melanoma liver metastases, ConA, WGA, succinylated WGA, and GSL II were strongly expressed.