Changes in complement component C3 glycosylation in type 1 diabetes complications
A group from Faculty of Pharmacy and Biochemistry, University of Zagreb, Zagreb, Croatia, etc. has reported about a new biomarker (c3.Asn939-N2H10) for type 1 diabetes (T1D) complications.
https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fendo.2023.1101154/full
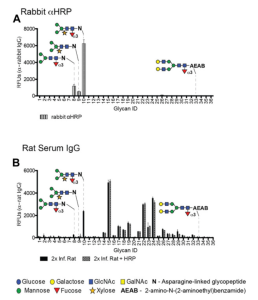
N-glycan profiles of complement component C3 have been profiled in 189 T1D subjects with different status of complication severity. The analysis was conducted by high-mannose glycoprotein enrichment from human blood serum using Con A lectin matrix, Glu-C digestion, glycopeptide purification and subsequent nano-LC-ESI-MS technique.
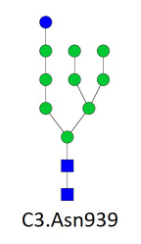
It was found that only one glycoform, C3.Asn939-N2H10, significantly changed in albuminuria and retinopathy, and also there was the biggest correlation between C3.Asn939-N2H10 and HbA1c.