A group from Department of Life Sciences, Pohang University of Science and Technology (POSTECH), Pohang, Gyeongbuk, Republic of Korea, etc. has reported that terminal fucosylation of haptoglobin (Hp) in cancer-derived exosomes could be a good biomarker for cholangiocarcinoma (CCA).
https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fonc.2023.1183442/full
Tumor glycosylation has been proposed as potential cancer biomarkers. Many studies have focused on characterizing the aberrant glycosylation of secreted molecules circulating the blood in their soluble form. In this study, it was shown that terminal fucosylation of membrane-bound components correlated with extracellular vesicles (EVs) correlates with CCA.
Glycomic analysis revealed that CCA-EV contained more α1-3/4 fucosylated glycans (terminal fucosylation) than normal EVs. Notably however, α1-6 fucose (core fucosylation) was comparable between samples. As a result, it was shown that the α1-3/4 fucosylation of β-Hp in cancer-derived EV can be used as biomarkers for early diagnosis of CCA as well as for the prediction of recurrence after surgery. And further, it was also shown that fucosylated EVs derived from CCA contribute to tumor progression.
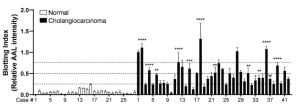
Diagnostic and prognostic value of EV-Hp fucosylation in CCA.
