Differences in maize rhizosphere microbiome due to drought and flooding stress
A group from Nanjing Agricultural University, China, etc. has reported about differences in maize rhizosphere microbiome due to drought and flooding stress.
https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmicb.2023.1295376/full
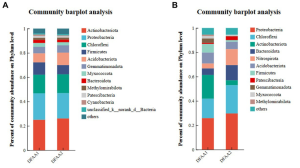
The results showed that
(1) the sum of the two phylums, Actinobacteria and Proteobacteri, accounted for nearly 50% existance, and
(2) Actinobacteria was the most dominant phylum in the two drought-flood abrupt alternation (DFAA) groups during the drought period and the rewatering period, and Proteobacteria was the most dominant phylum during the flooding period and the harvest period.
For your info., DFAA1 group means a trace rainfall to heavy rain condition and DFAA2 means a continuous drought to flooding condition.