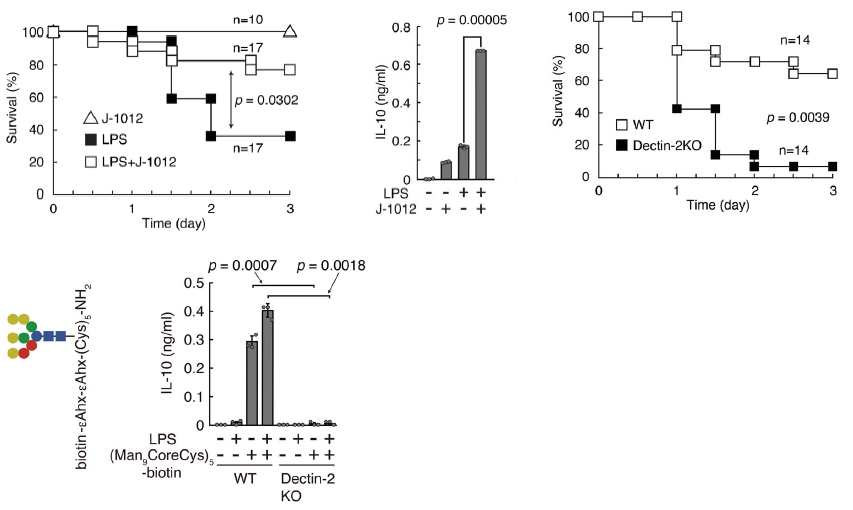
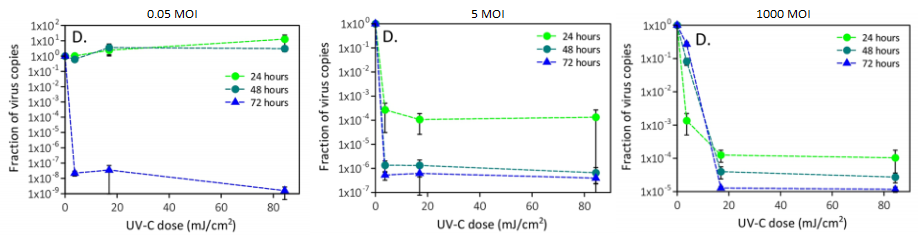
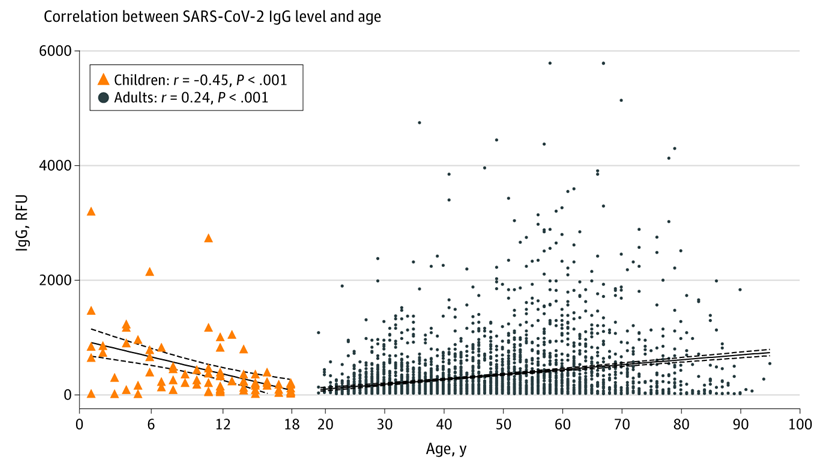
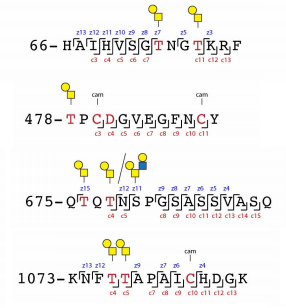
Diagnostic accuracy of COVID-19 Chest CT images with using Deep Learning methodology
A group from Sejong University, Seoul, etc. has reported on the accuracy of COVID-19 diagnosis in chest CT images with applying Deep Learning.
https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0249450
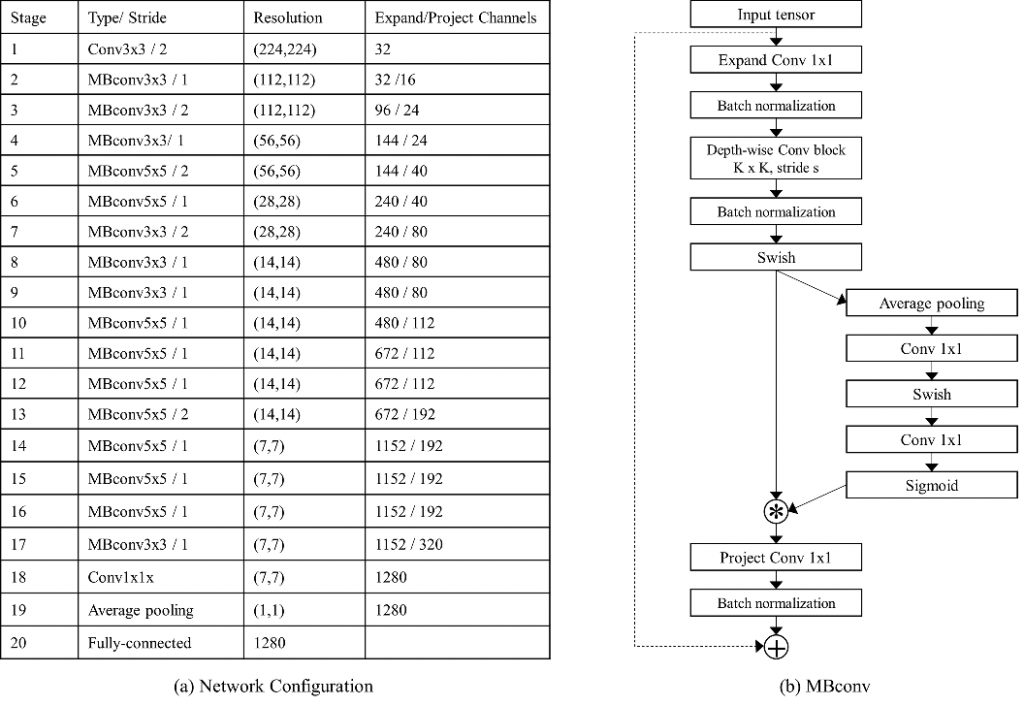
The neural network using in Deep Learning was composed of 20 stages, and convolution and pooling functions were incorporated. The resolution of the input images were (224 x 224, and the sizes of convolution were (3 x 3)and(5 x 5). The obtained overall accuracy was 99.83%(sensitivity=0.9286, specificity=0.99). In the future, it will be accelerate to adopt Deep Learning in diagnostic applications.