A group from Kyoto University has reported that the cell surface N-glycan (mannose core) of Candida albicans works anti-inflammatory in sepsis.
https://www.nature.com/articles/s42003-021-01870-3
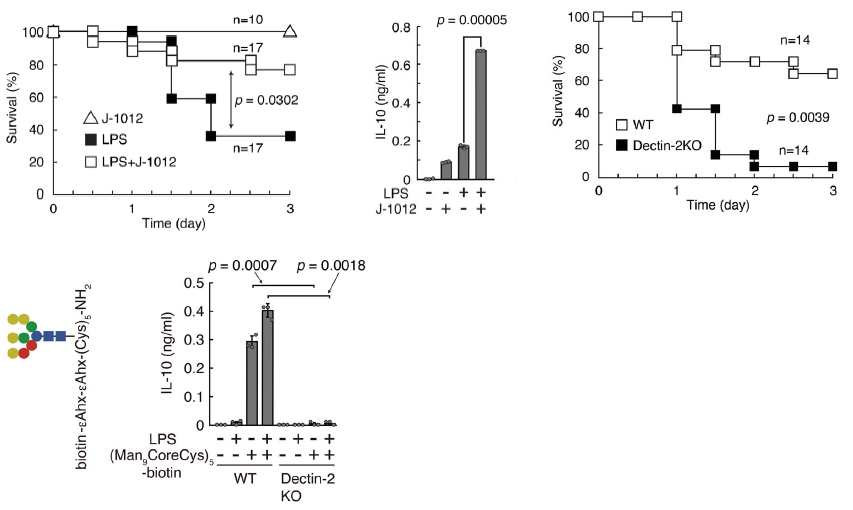
Sepsis was induced by lipopolysaccharide(LPS)in mouse, and it was demonstrated that purified mannoprotein of Candida albicans stratn J-1020 works anti-inflammatory. Injection of the extracted mannoprotein from J-1020 improved survival greatly. It was found that anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10 was up-regulated by the injection of J-1020 at this time. It was also confirmed that these phenomena were induced by the interaction between mannoprotein of J-1020 and C-type lectin Dectin-2. When Dectin-2 was knocked out, the survival decreased greatly, and J-1012 mannoprotein did not affect IL-10 production. Further, it was suggested the mannose core of Candida albicans N-glycan is recognized by Dectin-2, leading to suppression of the early onset of septic responses.