Four types of coronavirus (OC43, HKU1, NL63 and 229E) are known as coronaviruses that cause common human colds. On the other hand, there are three types of coronaviruses (SARS-CoV, SARS-CoV-2, MERS-CoV) that are highly pathogenic. As you know, SARS-CoV-2 is the new coronavirus that caused the pandemic (COVID-19) from the end of 2019.
A group of Univ. of Washington etc. has report on neutralize antibodies that respond broadly to this type of β-coronaviruses.
https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.12.29.424482v2.full
The cross-reaction of antibodies is a well-known phenomenon, but for example, antigen testing using antibodies does not accurately identify antigen viruses when there is such a cross-reactivity. However, a strong cross-reactivity can help inhibit the infection of new viruses if the antibodies of past-affected viruses are still active.
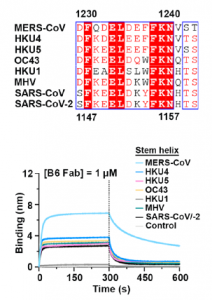
A monoclonal antibody against coronavirus, which was named as B6, has a wide range of cross-reactivity and is attracting attention as a neutralize antibody. As shown in the figure below, this B6 antibody has an amino acid sequence common to these β-coronaviruses in the S2 sub unit as an epitope, and the relevant part is involved in membrane fusion in the event of infection. The MHV in binding curve in the figure below is a mouse hepatitis virus belonging to the coronavirus family.