The common knowledge in HIV infection is that two types of receptors are related to the infection to CD4+ T cells. First of all, an envelop glycoprotein of HIV called gp120 binds to the first receptor CD4, then binds to the second receptor, CCR5 or CXCR4, and initiates membrane fusion between HIV and T cell. A group from University of Sydney, etc. has reported what major HIV target cells in human anogenital tissues in the HIV infection.
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-021-22375-x
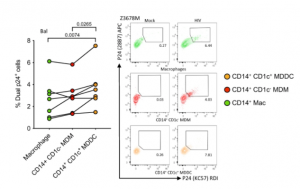
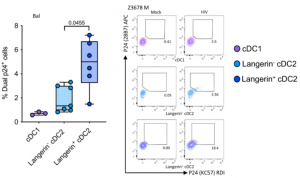
Authors have identified two types of cells, one is D14+CD1c+ monocyte-derived dendritic cells(CD14+CD1c+MDDC, and the other is Langerin-expressing dendritic cells 2(Langerin+ cDC2). Langerin is a C-type lectin which is selectively expressed on langerhans cells (LC), a subset of dendritic cells distributing in dermis and mucosa. The binding specificity of langerin is known to be high mannose and galactose with sulfated 6th site. Furthermore, it was found that HIV infection was correlated with Siglec-1 expression on CD14+ MDDC. In this way, these cells bind HIV and mediate efficient HIV uptake, and transfer to CD4+ T cells.
From a view point of glycan and lectin, it is so important to understand the relationship between C-type lectins on host cells and HIV gp120 glycoproteins.