A group from Niigata University, etc. has reported that Dectin-2 is related to Infection of Influenza virus and the induction of inflammatory responses.
https://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/article/biomedres/42/2/42_53/_pdf/-char/en
Although the importance of relationship between hemagglutinin (HA) and sialic acids has been emphasized, agents targeting HA and sialic acids are not effective in suppressing severe influenza unless they are administered within 48 h after symptoms begin. Antigen-presenting cells (APCs), such as dendritic cells (DCs) and macrophages, recognize pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) and damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) of dead cells or damaged tissues, and activate inflammatory immune responses. Toll-like receptors (TLRs), Nod-like receptors (NLRs), and C-type lectin receptors (CLRs) are known as such pattern recognition receptors.
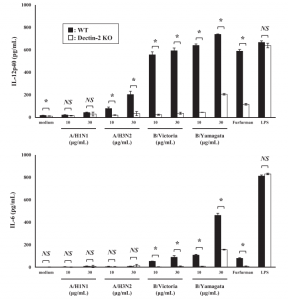
Since HA is strongly high mannosylated, there must be a signal path activating inflammatory immune responses through the interaction between C-type Lectins and glycosylated. C-type Lectin family includes DC-SIGN, Dectin-1, Dectin-2, Mincle, etc. Authors have found that Dectin-2 expressed on BM-DCs recognizes glycosylated HA from the type A and type B strains, and induce production of inflammatory cytokines. Dectin-2 recognized high mannose polysaccharides.
A figure below shows that production of inflammatory cytokines is greatly reduce by knocking out Dectin-2.