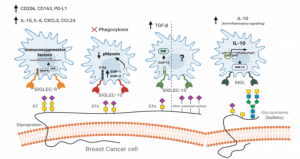
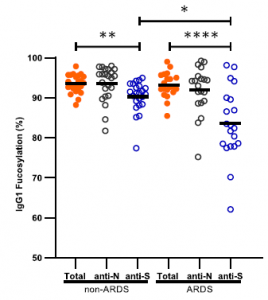
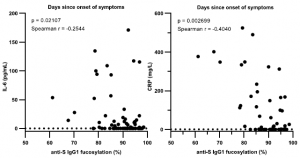
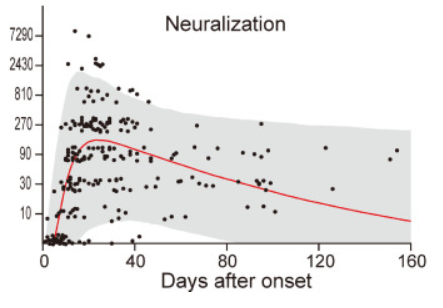
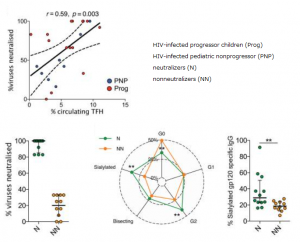
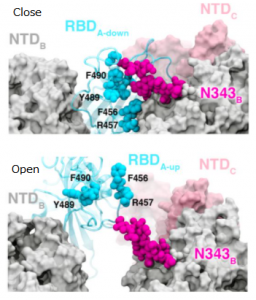
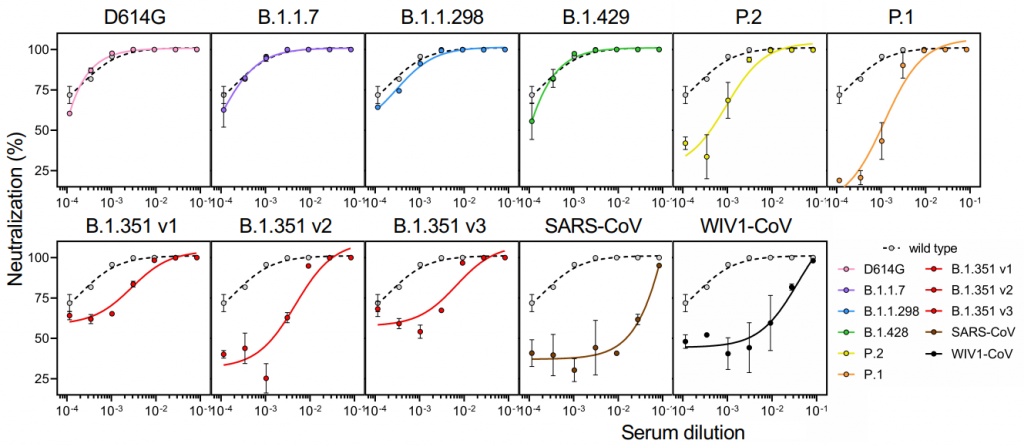
SARS-CoV-2 UK variant (B.1.1.7) and South African variant (B.1.351) have stronger affinity to ACE2
Two types of recently appeared SARS-CoV-2 variants named UK variant (B.1.1.7) and South African variant (B.1.351) are very famous. And, there have been several reports on the efficacy of Pfizer’s and Moderna’s vaccines for those variants. On Feb. 6th, 2021, a short report was introduced in this blog that the current vaccines are not so affected by UK variant, but are greatly affected by South African variant.
A group from School of Medicine, Stanford University has reported that these variants have higher affinity to ACE2, in concrete, about two times with B.1.1.7 and about five times with B.1.351.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7924271/