On a blog article posted on May 1st, 2021, it was introduced that the fucosylation of HIV gp120-specific IgG is decreased in some HIV patients.
A group from University of Amsterdam, etc. has indicated that the fucosylation of SARS-CoV-2 S-protein-specific IgG is also decreased in some COVID-19 patients.
https://science.sciencemag.org/content/371/6532/eabc8378.long
It is well known that the effector functions such as ADCC and ADCP are reinforced with afucosylation of IgG Fc. If this moves in a positive direction, it can accelerate virus clearance. This would be exactly true in the case of HIV infection. However, immunity potentially behave as double-edged swords, and in the case of COVID-19, it was thought that afucosylation of IgG might promote the production of pro-inflammatory cytokine IL-6 resulting in cytokine storm and tissue damages.
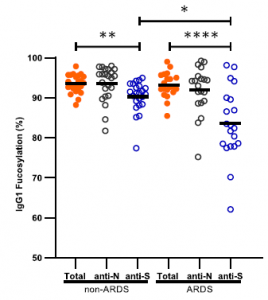
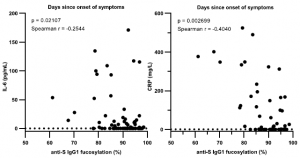
In the figures below, it is shown that when Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) is developed, fucosylation of S-protein specific IgG is decreased, although there is no change in fucosylation of total IgG. This means that the effector functions of antibodies are enforced. And further, when afucosylation of IgG proceeds, IL-6 production is accelerated and CRP as an Inflammatory marker gets higher.