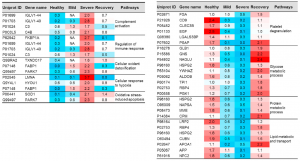
A group from Beijing Proteome Research Center, etc. has reported results of quantitative and comparative urine proteome analysis from healthy individuals, mild and severe COVID-19 positive patients.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33688631/
A total number of 2656 proteins was identified from healthy control samples. There were 1008 proteins being commonly identified and quantified among healthy, mild and sever cases. However, 211 and 63 proteins were uniquely expressed in COVID-19 patients and recovery samples.
Some proteins increased in COVID-19, but some proteins decrease inversely in COVID-19.
Typical examples are listed below. However, from a view point of this blog Admin, there is some question if urine proteome can be used as a diagnostic tool, because it seems that urine proteome can not discriminate severity of COVID-19 from moderate, mild, to sever. But, it would definitely contribute to elucidation of COVID-19 pathology. The fact that the urine proteome of recovered patients is not the same as healthy individuals would suggest that the aftereffects are remaining for a longer time.
IGLV1-40: 14 times higher in the severe COVID-19
FKBP1A: 13 times higher in the severe COVID-19
LUNA: 37 times higher in the severe COVID-19
PARK7: 7 times higher in the severe COVID-19
CD9: 1/12 times lower in the sever COVID-19
EGF: 1/25 times lower in the sever COVID-19
MME: 1/18 times lower in the sever COVID-19
CUBN: 1/19 times lower in the sever COVID-19