A group from National Key Laboratory of Crop Biology, College of Horticulture Science and Engineering, Shandong Agricultural University, Shandong, China has reported on Bacillus amyloliquefaciens QSB-6 strain isolated from apple orchard soils and its effect on apple tree roots and disease.
https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmicb.2021.746799/full
Authors compared effects of 4 types of soils on apple tree roots.
- untreated soil from a 31-year-old orchard (CK1)
- the same soil fumigated with methyl bromide (CK2)
- the same soil treated with the manure carrier only (T1)
- the same soil treated with Bacillus amyloliquefaciens strain QSB-6 manure treatment (T2)
Interestingly, the CK2, T2, and T1 treatments significantly promoted the growth of apple tree roots, and the relative treatment effects were ranked from high to low: CK2 > T2 > T1 > CK1.
The number of rhizobacteria increased significantly after T2 treatment by 9.64 times higher in T2 than in CK1, and soil fungal numbers were reduced significantly by 85.58% (in CK2) and 81.74% (in T2) compared with CK1.
Extracellular metabolites from strain QSB-6 showed a strong inhibitory effect on Fusarium hyphal growth and spore germination as shown below.
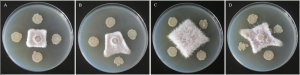 (A) Fusarium proliferatum, (B) Fusarium solani, (C) Fusarium verticillioides, (D) Fusarium oxysporum
(A) Fusarium proliferatum, (B) Fusarium solani, (C) Fusarium verticillioides, (D) Fusarium oxysporum
In summary, B. amyloliquefaciens QSB-6 has a good inhibitory effect on Fusarium in the soil and can significantly promote apple tree root growth. It has great potential as a biological control agent against apple disease.
