RT-PCR testing for the new coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) is critical to the number of days since the first signs of infection and how samples are obtained.
RT-PCR is Gold Standard for testing for the new Coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2).
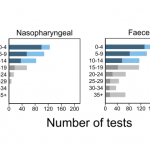
However, you need to be careful about RT-PCR results. Rt-PCR tests from the nasopharyngeal are highly reliable until the fourth day after signs of infection, but after 10 days, the detection accuracy falls and the probability of false negative gets very high.
On the other hand, the test from the feces is not reliable at the beginning of infection, but it is possible to detect the virus even after a number of days of infection, and it is better to use feces than to obtain samples from the nasopharyngeal to determine whether the virus has been eliminated in the end.
https://bmcmedicine.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12916-020-01810-8
In this figure, dark blue and dark gray indicate virus detection two weeks before and after infection, respectively, and light blue and light gray indicate false negatives.