A group from Lehigh University, Bethlehem, USA has reported on pulling force between RBD of various SARS-CoV-2 variants and ACE2 taking into consideration of glycans.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8328061/
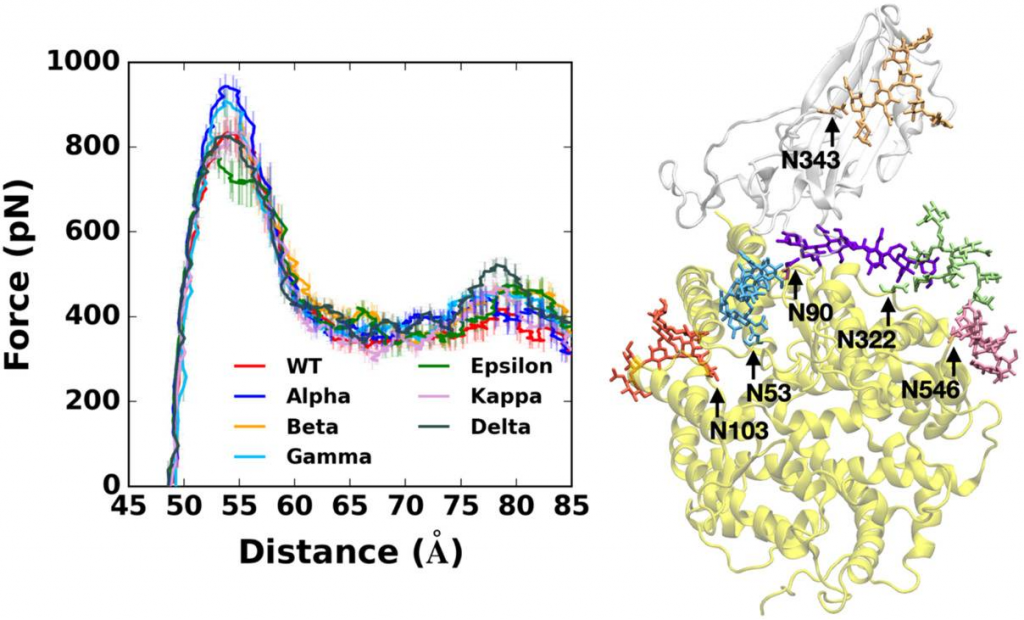
Pulling force analysis using molecular dynamics simulations was performed on RBD-ACE2 complexes as a function of distance between the centers of mass of RBD and ACE2 proteins. Fully-glycosylated S RBD-ACE2 complex model was employed for the pulling simulation, and the following variants were covered.
Alpha variant (first identified in United Kingdom, B.1.1.7: N501Y),
Beta variant (first identified in South Africa, B.1.351: K417N, E484K, N501Y),
Gamma variant (first identified in Japan/Brazil, P.1: K417T, E484K, N501Y),
Delta variant (first identified in India, B.1.617.2: L452R, T478K)),
Epsilon variant (first identified in US-California, B.1.427: L452R) ,
Kappa variant (first identified in India, B.1.617.1: L452R, E484Q)),
Alpha variant requires the highest force for initial separation from ACE2, followed by Beta and Gamma variants or Delta variant. K417N/T mutations of Beta and Gamma appear to make the RBD-ACE2 interactions less strong compared to Alpha variant. In addition, Epsilon variant is likely to be relatively easily dissociated from ACE2 than others due to its destabilized RBD structure upon the L452R mutation. In addition, Delta variant specifically shows stronger interactions with ACE2 than other variants at a relatively far distance between RBD and ACE2.
The Delta variant, interestingly, shows distinct features that are not found in other variants. Upon the T478K mutation, it requires the highest force for the RBD-ACE2 complex to be completely dissociated at D = 78 Å. In order to see what makes the difference, the number of contacts between RBD residue 478 and heavy atoms of selected key interacting residues of ACE2 was calculated. RBD Delta exclusively makes more contacts with ACE2 than other variants. Delta K478 retains contacts with ACE2 P84 and M82 at D = 78 Å, but Epsilon T478 already lost such interactions. It is possible that residue 478 located in the flexible loop could first have a chance to contact with ACE2, and the stronger interactions of Delta K478 with ACE2 could explain the reason why the proportion of Delta variant is recently dramatically being increased with high infectivity.