A group from Harvard Medical School, etc. has reported on the effects of glycosylation and disulfide bonding of SARS-CoV-2 Spike protein onto infectivity and susceptibility to antibody inhibition.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33821278/
There are 22 N-glycosylation sites, 10 O-glycosylation sites and 15 disulfide bonding in the spike protein.
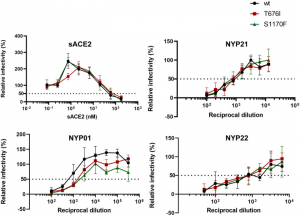
In this paper, it was shown experimentally how the mutations at O-glycosylation sites(676, 1170)affect binding to ACE2 and titer of sera from convalescing SARS-CoV-2-infected individuals. Let me introduce that point for this blog readers. The evaluated mutations were T676I and S1170F. As shown below, it seems that these mutations do not affect so much.