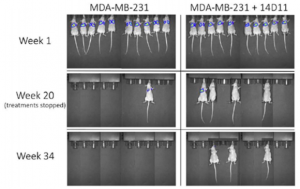
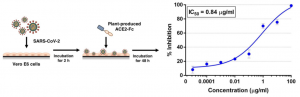
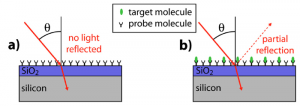
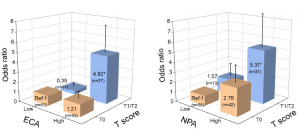
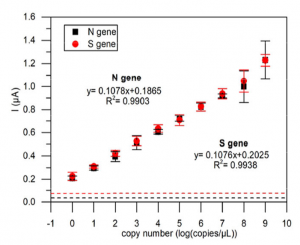
Monochronal Antibody Cocktails would be effective in rapidly mutating RNA viruses such as SARS-CoV-2
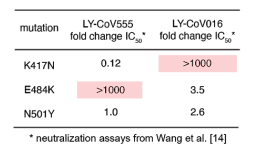
A group from Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center, etc. has investigated the effect of genomic mutations onto two types of monochronal antibodies (LY-CoV555 and LY-CoV016) against RBD of SARS-CoV-2.
https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2021.02.17.431683v1
It was found that LY-CoV016 is very weak for K417N mutation, and LY-CoV555 is so weak for E484K mutation. In both cases, IC50 increased more than 1,000 times with these mutations. Therefore, a strategy using antibody cocktails with different monochronal antibodies with different target epitopes would be quite effective in developing therapeutic drugs for rapidly mutating RNA viruses such as SARS-CoV-2.