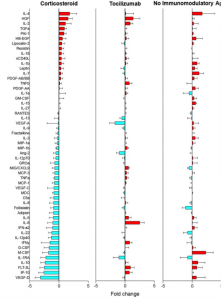
Systemic corticosteroids are better than Tocilizumab (Actemula) in the treatment of the new coronavirus (COVID-19)
When the new coronavirus (COVID-19) becomes severe, cytokine storms occur and develop acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). For this treatment, from the viewpoint of immune control, il-6 inhibitors such as tocilizumab (actemula) and steroids that suppress inflammation are used.
The Yale School of Medicine group reports from randomized, placebo-controlled trials that systemic corticosteroids are more therapeutic and the effects of tocilizumab are not clear.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7781335/
As shown in the figure below, the behavior of covid-19 biomarkers is very different between corticosteroids and tocilizumab. Perhaps, it is because the effect is limited even if a single cytokine is inhibited.