In the lectin pathway as one of innate immunities, pattern recognition molecules (PRMs) (i.e., mannose-binding lectin (MBL), ficolins, and collectin-10/-11) bind to pathogens recognizing specific molecular structures on the membranes, make complexes with MAPSs, activate complements sequentially, and finally form Membrane Attack Complex (MAC) on the membranes to kill pathogens.
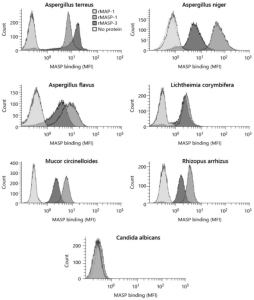
However, a group from University of Copenhagen, etc. has reported a new pathway in which MAPSs directly bind to pathogens and activate the complement system using Aspergillus fumigatus as a pathogen. This means that a new pathway in the complement system was discovered showing MASP-1 and MASP-3 have dual functions as enzymes and as PRMs
https://www.karger.com/Article/FullText/514546