A group from Laboratory of Biochemistry and Glycobiology, Department of Biotechnology, Ghent University, Belgium, etc. has reported about a ConA-like mannose-specific lectin, Cvill, isolated from Canavalia villosa seeds.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10649158/
Cvill is a ConA-like mannose-specific lectin isolated from Canavalia villosa seeds.
The lectin structure is composed of 237 amino acid residues, similar to other ConA-like lectins .
Cvill exhibits the typical legume lectin fold, also known as a β-sandwich, characterized by the presence of two superimposed beta sheets, resembling a sandwich. These beta sheets consist of antiparallel strands, with one beta sheet formed by six long, flat beta strands and the other by seven curved strands.The arrangement of dimers and tetramers in the quaternary structure was predicted.
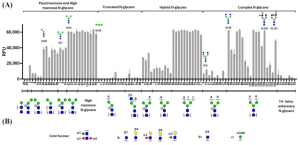
Glycan array experiments indicated that Cvill exhibits affinity for terminal α-mannosyl residues and the tri-mannosidic core of N-glycans.
Cvill demonstrated dose-dependent cytotoxicity against all tested cell lines and this toxicity was carbohydrate-mediated. Cvill presented IC50 values of 97.0 μg/mL after 48 h incubation period for HeLa ells. Cvill also affected the viability of the fibrosarcoma (HT1080 cells) and the NHDF cells with IC50 values of 116.08 μg/mL and 108.34 μg/mL after a 48 h incubation period.