A group from Iwate Biotechnology Research Center, Kitakami, Iwate, Japan, etc. has reported that OsRMC binding to CBM1 of a blast fungal xylanase blocks access to cellulose, resulting in the inhibition of xylanase enzymatic activity.
https://journals.plos.org/plospathogens/article?id=10.1371/journal.ppat.1010792
The plant apoplastic space is filled with the primary cell wall, mainly composed of the polysaccharides cellulose, hemicellulose, and pectin. Hemicellulosic polysaccharides play an important role in controlling the physical properties of the cell wall. Xyloglucan in dicotyledonous and xylan in monocotyledonous plants are the major hemicellulosic polysaccharides by quantity and strengthen the cell wall by forming cross-bridges between cellulose microfibrils. A cell wall composed of heteropolysaccharides also provides a physical barrier against plant pathogen invasion.
Plant pathogenic fungi secrete a battery of cell wall-degrading enzymes (CWDEs) that catalyze hydrolytic and oxidative degradation of plant cell wall polysaccharides, assisting fungal penetration and colonization.
Plants have evolved various activity-inhibiting proteins as a defense against fungal cell wall-degrading enzymes (CWDEs), but how plants counteract the function of fungal enzymes containing carbohydrate binding modules (CBMs) remains unknown. Here, it was demonstrated that OsRMC, a CBM1-interacting protein (CBMIP) of rice (Oryza sativa), binding to CBM1 of a blast fungal xylanase blocks access to cellulose, resulting in the inhibition of xylanase enzymatic activity. Where, OsRMC is a member of the Cysteine-rich repeat secretion proteins (CRRSPs) containing two DUF26, and binds mannose as well as CBM1.
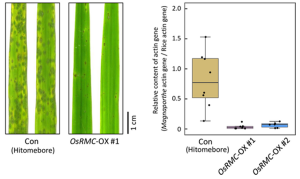
(LEFT)Rice leaves of wild-type (Hitomebore) control (Con) and OsRMC-overexpressing (OsRMC-OX) lines 4 days after inoculation of M. oryzae inoculation.
(RIGHT)The amount of M. oryzae fungal mass in rice leaf was monitored by quantifying the ratio of M. oryzae genomic DNA to rice genomic DNA obtained by PCR.
