Lactoferrin is an iron-binding glycoprotein with a molecular weight of 80,000 contained in milk. It is found in mammalian milk (especially colostrum), including human, but is also found in tears, saliva, pancreatic fluid and other exocrine fluids and neutrophils in adults. Lactoferrin is also known to maintain and improve health, including immune regulation, antiviral function,
lactobacillus bifidus proliferation, iron absorption regulation associated with iron binding ability, anti-inflammatory action, and lipid metabolism improvement action.
A group from University of Arizona, Tucson etc. has reported that lactoferrin actually shows antiviral effects against SARS-CoV-2, and what is the mechanism behind it.
https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/22221751.2021.1888660
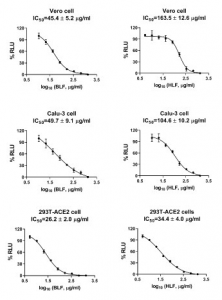
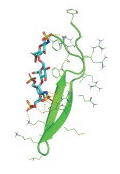
Using ACE2 overexpressed 293 T cells, Vero E6 cells, and Calu-3 cells, they show the inhibitory activity of lactoferrin on infection of SARS-CoV-2 in vitro. They have also verified using a molecular docking method that the mechanism of infection inhibition is blocking SARS-CoV-2 binding to heparan sulfate, which is a co-receptor of ACE2. Heparan sulfate has a negative charge and is thought to bind to a positively charged region (17 to 41 rest regions) present in the NTD of the SARS-CoV-2 S-protein. In the figures below, BLF=Bovine lactoferrin and HLF=Human lactoferrin. The lower right hand side figure shows a molecular docking image of heparin dp4 with bovine lactoferricin.