A group from Department of Mathematics, Michigan State University, MI, USA, etc. has reported on Infectivity, vaccine breakthrough, and antibody resistance of SARS-CoV-12 Omicron variant.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8647651/
Infectivity:
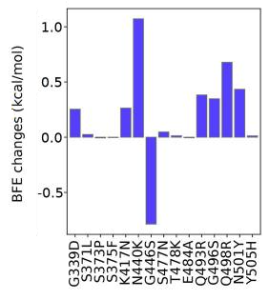
The Infectivity of SARS-CoV-2 is mainly determined by the binding affinity of the ACE2 and RBD complex, although the furin cleavage site plays a crucial role as well. Omicron has three mutations at the furin cleavage site and 15 mutations on the RBD, suggesting a significant change in its infectivity. Changes in the infectivity of Omicron were analyzed by examining the Binding free energy (BFE) changes of the ACE2 and S protein complex induced by 15 Omicron RBD mutations. As a result, Omicron is to be about 2.8 times as infectious as the Delta (i.e., BFE change: 1.57kcal/mol).
Vaccine breakthrough:
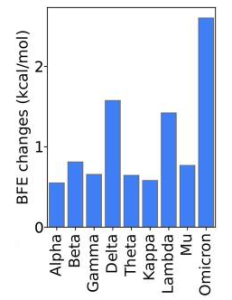
A molecule-based data-driven analysis as done about Omicron’s impact on vaccines through a library of 132 known antibody and S protein complexes. Changes in the binding free energy induced by 15 RBD mutations on these complexes were evaluated to understand the potential impact of Omicron’s RBD mutations to vaccines. This study does not include a few known antibody-S protein complexes that are far away from the RBD, such as those in the N-terminal domain (NTD), due to limited experimental data in the antibody library. As a result, Omicron’s vaccine-escape capability will be about twice as high as that of the Delta variant.
Antibody resistance:
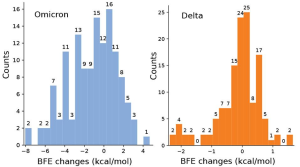
Omicron will have a very mild negative impact on the Regeneron cocktail.