A group from Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China, etc. has reported on sero-positivity and neutralizing activity of SARS-CoV-2 infected individuals over one year.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8242354/
A total of 162 serum samples from 76 SARS-CoV-2-infected individuals including some of the very earliest COVID-19 patients were collected in our study.
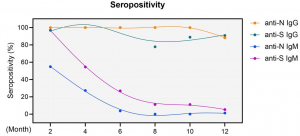
The SARS-CoV-2 Spike- and Nucleocapsid-specific IgM started at intermediate to high levels (96.8 and 54.8%, respectively) early after infection and rapidly and dramatically waned over time. At the end of the one-year observation period, only four cases remained positive for both anti-S and anti-N IgM, resulting in residual positivity rates of 5.3% and 1.3%, respectively. Conversely, the overall sero-positivity for IgG antibodies in convalescent individuals remained very stable with 90.8% and 88.2% sero-positivity for anti-S and anti-N IgG, respectively, persisting for one year
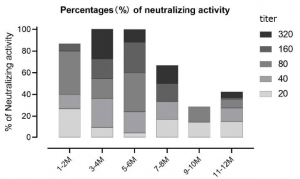
SARS-CoV-2-specific neutralizing activity was measured by virus neutralization assays. The results showed that the majority of patients (57.5%) did not exhibit detectable neutralization capacities one year after the symptom onset. The proportion of patients with high titers of neutralizing antibodies (defined by titers exceeding 1:160) was highest 3-4 months after symptom onset. Among the minority of patients who still had detectable nAb (42.5%), most individuals showed rather low nAb titers (≤1:80). Only very few (5.5%) patients exhibited strong neutralizing titers at or above 1:320.