A group from IRCCS Azienda Ospedaliero-Universitaria di Bologna, Italy has reported on differences in lung microbiome between COVID-19 patients and COVID-19 negative persons.
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-021-89516-6
Several indexes have been developed to discuss about similarity among groups and characteristics of each group.
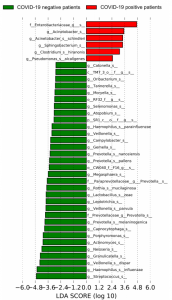
Similarity Percentage analysis highlighted that the lung microbiome of COVID-19 patients was characterized by a higher relative abundance of Pseudomonas spp. compared to COVID-19-negative persons. On the other hand, the lung microbiome of COVID-19-negative persons was mainly characterized by the enrichment of lung commensal bacteria (such as Haemophilus influenzae, Veillonella dispar, Granulicatella spp., Porphyromonas spp., and Streptococcus spp).
The linear discriminant analysis (LDA) highlighted that the lung microbiome of COVID-19 patients was characterized by the presence of Pseudomonas alcaligenes, Sphingobacterium spp., Clostridium hiranonis, Acinetobacter schindleri, Enterobacteriaceae of unknown genus and Acinetobacter spp.
A common feature between these two analysis indexes was Pseudimonas spp. This means that enrichment of opportunistic gram-negative pathogens frequently associated with multidrug resistance increase in COVID-19 patients and the lung commensal bacteria decrease inversely.