There have been some papers reporting that C-type Lectins could be SARS-CoV-2 infection receptors as well as well-know ACE2.
Harvard Medical School, July 30, 2020
https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.07.29.227462v1
Boston University, Dec. 9, 2020
https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.06.22.165803v2
There was a review paper from Boston University, (Dec. 22, 2020) in addition to the above paper, let me introduce two kinds of interesting data for your reference.
https://www.mdpi.com/2079-7737/10/1/1
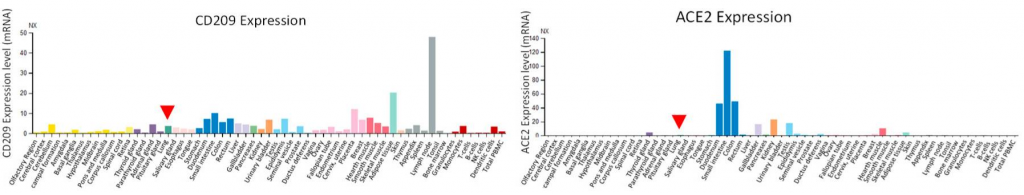
Although ACE2 is a really important virus receptor, the expression level of ACE in lung is very low, however, CD209 and CD209L are more broadly expressed in human tissues rather than the ACE2.
A result of infection experiments using SAR-CoV-2 pseudotyped lentivirus and HEK293 cells overly expressing CD209L, CD209, and ACE2 is also shown below.
Taking these things into consideration, it would be clear that CD209 and CD209L could mediate SARS-CoV-2 entry as infection receptors even for tissues lacking ACE2 expression.
The CRDs of C-type Lectins (DC-SIGN, L-SIGN) recognize strongly high mannose type glycans.