A group from Molecular Microbiology and Immunology, Brown University, RI. 02912, USA, etc. has reported anti-Chitinase 3-like-1(CHI3L1) and the small molecule CHI3L1 inhibitor kasugamycin both inhibited lung epithelial infection with SARS-CoV-2.
https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2022.01.21.477274v1
It was thought that therapies that target the host factors involved in SARS-CoV-2 infection like CHI3L1 can contribute to the control of COVID 19 induced by all viral variants that use ACE2. To test this hypothesis, pseudoviruses that expressed Spike proteins from the α, β, γ, δ and o variants were prepared, and the ability of CHI3L1-based interventions to modify their ability to infect human lung epithelial cells were assessed. These studies demonstrate that CHI3L1 augments the expression and accumulation of ACE2 and Spike priming proteases (SPP) and augments epithelial infection by the α, β, γ, δ and o pseudovirus variants. They also demonstrate that anti-CHI3L1 and the small molecule CHI3L1 inhibitor kasugamycin both inhibit the expression and accumulation of epithelial ACE2 and SPP and, in turn, inhibit epithelial infection by pseudoviruses that contain the α, β, γ, δ and o Spike proteins.
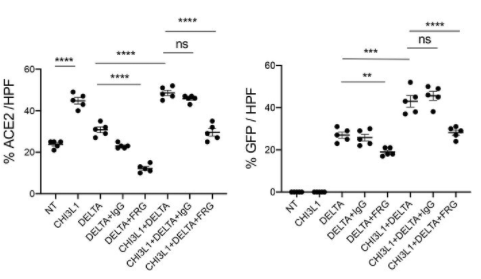
It was demonstrated that CHI3L1 augmented Calu-3 cell ACE2 accumulation and delta pseudovirus infection, and also that FRG(anti-CHI3L1) abrogated the expression of ACE2 and delta pseudovirus infection.
The similar anti-virus activity was observed also in the case of Kasugamycin. It effectively inhibited the uptake of pseudovirus with the alpha, beta, gamma or delta Spike protein mutations.
